Unix I/O
open(const char *pathname, int flags, mode_t mode);
O_RDONLY, O_WRONLY, O_RDWR
S_IRWXU, S_IRUSR, S_IWUSR
read(int fd, void *buf, size_t count);
write(int fd, const void *buf, size_t count);
stat(const char *pathname, struct stat *statbuf);
struct stat {
dev_t st_dev; // Device
ino_t st_ino; // inode
mode_t st_mode; // Protection and file type
nlink_t st_nlink; // Number of hard links
uid_t st_uid; // User ID of owner
gid_t st_gid; // Group ID of owner
dev_t st_rdev; // Device type (if inode device)
off_t st_size; // Total size, in bytes
unsigned long st_blksize; // Blocksize for filesystem I/O
unsigned long st_blocks; // Number of blocks allocated
time_t st_atime; // Time of last access
time_t st_mtime; // Time of last modification
time_t st_ctime; // Time of last change
};共享文件
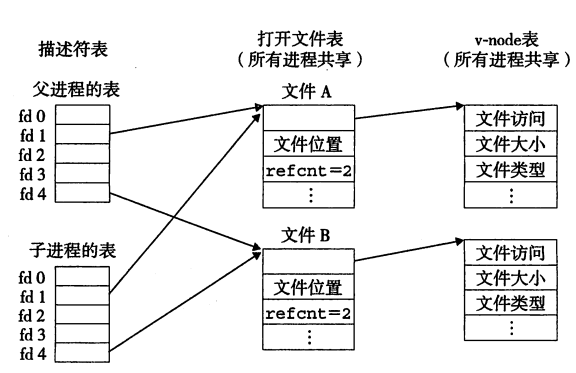
描述符表是进程独有
文件位置(file position):文件头起始的偏移量
重定向
dup2(int oldfd, int newfd);
ls > text.txt STDOUT_FILENO指向 text.txt
ls < text.txt STDIN_FILENO指向 text.txt